Interfaces and components for building a virtual hardware platform. More...
|
Classes | |
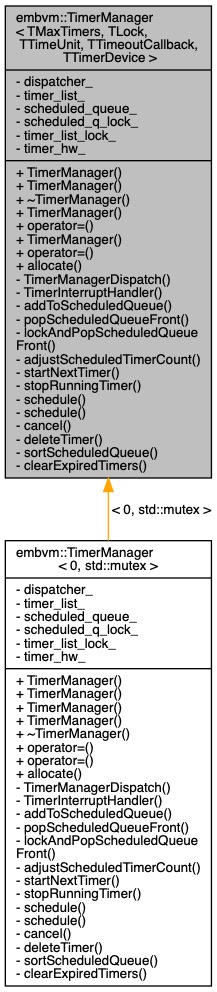
| class | embvm::TimerManager< TMaxTimers, TLock, TTimeUnit, TTimeoutCallback, TTimerDevice > |
| Timer Manager Class. More... | |
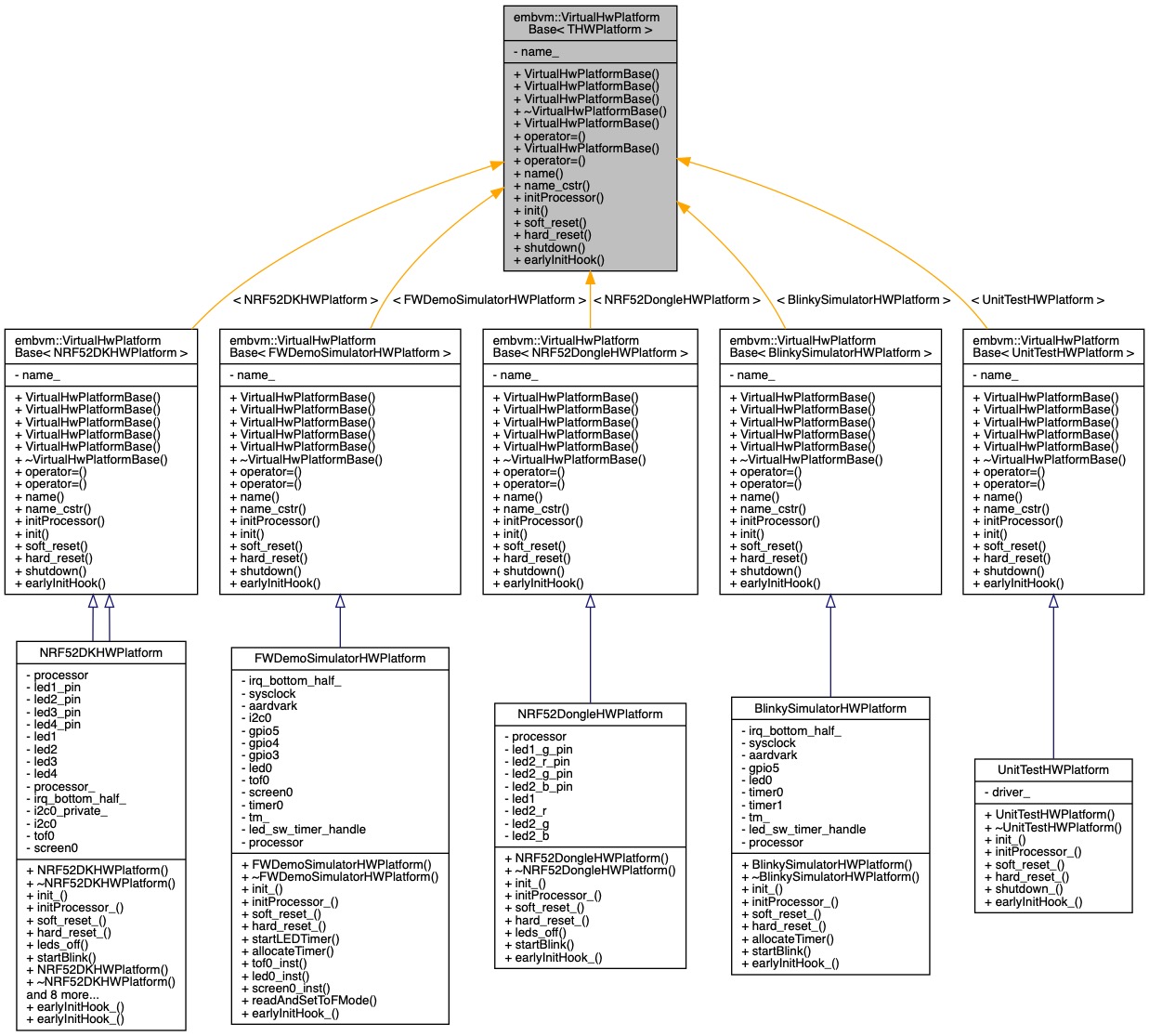
| class | embvm::VirtualHwPlatformBase< THWPlatform > |
| Virtual Hardware Platform Base. More... | |
Detailed Description
Interfaces and components for building a virtual hardware platform.
Class Documentation
◆ embvm::TimerManager
| class embvm::TimerManager |
template<const size_t TMaxTimers = 0, typename TLock = embutil::nop_lock, typename TTimeUnit = embvm::timer::timer_period_t, typename TTimeoutCallback = stdext::inplace_function<void()>, typename TTimerDevice = embvm::timer::Timer>
class embvm::TimerManager< TMaxTimers, TLock, TTimeUnit, TTimeoutCallback, TTimerDevice >
Timer Manager Class.
The Timer Manager takes a hardware timer and uses it to produce a number of software timers.
An alternative structure accomplishing this task is the callback_timer provided by ETL in callback_timer.h, which uses a tick() function: https://www.etlcpp.com/callback_timer.html
- Template Parameters
-
TMaxTimers The maximum number of software timers that can be created. Size 0 indicates dynamic memory will be used. All other sizes will enable static memory allocation. TLock The type of lock interface to use. Default is embutil::nop_lock, which disables locking. To enable locking, declare TimerManager with a functional lock type. using TimerManager_t = embvm::TimerManager<0, std::mutex>;TTimeUnit The time-keeping units. The default embvm::timer::timer_period_tis inherited from the Timer base class. This can be overriden to provide a specific timer resolution (e.g. 1ms instead of 1us). TTimeUnit is limited by the granularity that the Timer can support.TTimeoutCallback The storage type for the callback function. TTimerDevice The type of timer device that this class will manage. The default Timer type is the base class that framework timers derive from.
Public Types | |
| using | DispatcherFunc = stdext::inplace_function< void(const TTimeoutCallback &)> |
| The function prototype for the Dispatcher. More... | |
Public Member Functions | |
| TimerManager (TTimerDevice &timer) noexcept | |
| Create a TimerManager without a dispatcher. More... | |
| TimerManager (TTimerDevice &timer, const DispatcherFunc &dispatcher) noexcept | |
| Create a TimerManager with a dispatcher. More... | |
| ~TimerManager () noexcept | |
| Destroy the TimerManager. More... | |
| TimerManager (const TimerManager &)=delete | |
| Deleted copy constructor. More... | |
| const TimerManager & | operator= (const TimerManager &)=delete |
| Deleted copy assignment operator. More... | |
| TimerManager (TimerManager &&)=delete | |
| Deleted move constructor. More... | |
| TimerManager & | operator= (TimerManager &&)=delete |
| Deleted move assignment operator. More... | |
| TimerHandle | allocate () noexcept |
| Allocate a new software timer. More... | |
Private Types | |
| using | TimeRep_t = typename TTimeUnit::rep |
| Alias for the time unit representation (e.g., uint32_t, uint64_t) More... | |
| using | TTimerQueueType = typename std::conditional<(TMaxTimers==0), std::list< delayInfo >, etl::list< delayInfo, TMaxTimers > >::type |
| Type definition for the underlying timer queue. More... | |
| using | TQueueHandle = typename TTimerQueueType::iterator |
| Convenience alias for the queue handle type. More... | |
| using | TScheduledQueueType = typename std::conditional<(TMaxTimers==0), std::vector< TQueueHandle >, etl::vector< TQueueHandle, TMaxTimers > >::type |
| Convenience type for the queue of scheduled timers. More... | |
Private Member Functions | |
| void | TimerManagerDispatch (const TTimeoutCallback &op) noexcept |
| TimerManager Default Dispatch Function. More... | |
| void | TimerInterruptHandler () noexcept |
| TimerManager's Timer Interrupt Handler. More... | |
| void | addToScheduledQueue (TQueueHandle handle) noexcept |
| void | popScheduledQueueFront () noexcept |
| void | lockAndPopScheduledQueueFront () noexcept |
| void | adjustScheduledTimerCount (TTimeUnit time_base) noexcept |
| void | startNextTimer () noexcept |
| auto | stopRunningTimer () noexcept |
| void | schedule (TQueueHandle handle, TTimeUnit delay, const TTimeoutCallback &func, embvm::timer::config config) noexcept |
| void | schedule (TQueueHandle handle, TTimeUnit delay, TTimeoutCallback &&func, embvm::timer::config config) noexcept |
| bool | cancel (TQueueHandle handle) noexcept |
| Returns false if no wait was scheduled or if the callback was already called Returns true if cancelled successfully. More... | |
| void | deleteTimer (TQueueHandle handle) noexcept |
| void | sortScheduledQueue () noexcept |
| void | clearExpiredTimers () noexcept |
Private Attributes | |
| const DispatcherFunc | dispatcher_ |
| TTimerQueueType | timer_list_ {} |
| TScheduledQueueType | scheduled_queue_ {} |
| TLock | scheduled_q_lock_ |
| TLock | timer_list_lock_ |
| TTimerDevice & | timer_hw_ |
Friends | |
| class | TimerManager::TimerHandle |
| The timer handle can call private TimerManager functions. More... | |
Member Typedef Documentation
◆ DispatcherFunc
| using embvm::TimerManager< TMaxTimers, TLock, TTimeUnit, TTimeoutCallback, TTimerDevice >::DispatcherFunc = stdext::inplace_function<void(const TTimeoutCallback&)> |
The function prototype for the Dispatcher.
The dispacher uses inplace_function regardless of static or dynamic memory allocation.
◆ TimeRep_t
|
private |
Alias for the time unit representation (e.g., uint32_t, uint64_t)
◆ TQueueHandle
|
private |
Convenience alias for the queue handle type.
A list iterator is used because iterators remain valid even with insertion/deletions
◆ TScheduledQueueType
|
private |
Convenience type for the queue of scheduled timers.
This queue is used to manage the list of currently scheduled timers.
The size of the scheduled queue will be <= the size of the allocated queue.
The type changes depending on whether static or dynamic memory allocation is being used (dynamic memory is indicated by TMaxTimers == 0)
◆ TTimerQueueType
|
private |
Type definition for the underlying timer queue.
This type is used to manage timers which have been allocated.
The type changes depending on whether static or dynamic memory allocation is being used (dynamic memory is indicated by TMaxTimers == 0)
Constructor & Destructor Documentation
◆ TimerManager() [1/4]
|
inlineexplicitnoexcept |
Create a TimerManager without a dispatcher.
Creating a TimerManager without a dispatcher will result in the manager invoking the functions.
When no dispatcher is used, timer callbacks are called directly by the TimerManager.
- Parameters
-
timer The timer hardware instance which the TimerManager will manage.
◆ TimerManager() [2/4]
|
inlineexplicitnoexcept |
Create a TimerManager with a dispatcher.
Creates a TimerManager class with an external dispatcher. When a timer expires, the TimerManager forwards the callback to the dispatcher, rather than executing the callbacks directly. Using a dispatcher improves timer latency, as the manager is focused only on managing timers.
- Parameters
-
timer The timer hardware instance which the TimerManager will manage. dispatcher Specifies a function which will dispatch all timer callbacks. Use TimerManager with a dispatch queue, or other type of system event queue.
◆ ~TimerManager()
|
inlinenoexcept |
Destroy the TimerManager.
On destruction, the TimerManager stops the underlying timer hardware and unregisters the TimerManager's timer interrupt callback.
◆ TimerManager() [3/4]
|
delete |
Deleted copy constructor.
◆ TimerManager() [4/4]
|
delete |
Deleted move constructor.
Member Function Documentation
◆ addToScheduledQueue()
|
inlineprivatenoexcept |
Referenced by embvm::TimerManager< 0, std::mutex >::schedule().
◆ adjustScheduledTimerCount()
|
inlineprivatenoexcept |
◆ allocate()
|
inlinenoexcept |
Allocate a new software timer.
Allocates a new timer in the TimerManager and returns a handle to the user.
- Returns
- A handle to the allocated software timer. The handle is used by the consumer to configure the timer. The TimerHandle's lifetime controls the timer's lifetime - once the TimerHandle leaves scope, the timer will be automatically unregistered.
Referenced by BlinkySimulatorHWPlatform::allocateTimer(), and FWDemoSimulatorHWPlatform::allocateTimer().
◆ cancel()
|
inlineprivatenoexcept |
Returns false if no wait was scheduled or if the callback was already called Returns true if cancelled successfully.
◆ clearExpiredTimers()
|
inlineprivatenoexcept |
◆ deleteTimer()
|
inlineprivatenoexcept |
◆ lockAndPopScheduledQueueFront()
|
inlineprivatenoexcept |
Referenced by embvm::TimerManager< 0, std::mutex >::cancel().
◆ operator=() [1/2]
|
delete |
Deleted copy assignment operator.
◆ operator=() [2/2]
|
delete |
Deleted move assignment operator.
◆ popScheduledQueueFront()
|
inlineprivatenoexcept |
◆ schedule() [1/2]
|
inlineprivatenoexcept |
◆ schedule() [2/2]
|
inlineprivatenoexcept |
◆ sortScheduledQueue()
|
inlineprivatenoexcept |
Referenced by embvm::TimerManager< 0, std::mutex >::addToScheduledQueue().
◆ startNextTimer()
|
inlineprivatenoexcept |
◆ stopRunningTimer()
|
inlineprivatenoexcept |
◆ TimerInterruptHandler()
|
inlineprivatenoexcept |
TimerManager's Timer Interrupt Handler.
TimerManager registers its own interrupt with the Timer hardware driver. When the timer interrupt fires, we account for the time that has elapsed, clear all scheduled timers, and restart the timer hardware with the next timeout request.
Note that this must work with an interrupt bottom-half handler because locking calls are used here. It cannot be called directly in an ISR context!
Referenced by embvm::TimerManager< 0, std::mutex >::TimerManager().
◆ TimerManagerDispatch()
|
inlineprivatenoexcept |
TimerManager Default Dispatch Function.
If no external dispatcher is provided, TimerManager has one which just executes the operation by default.
- Parameters
-
op The callback function object to execute.
Friends And Related Function Documentation
◆ TimerManager::TimerHandle
|
friend |
The timer handle can call private TimerManager functions.
Member Data Documentation
◆ dispatcher_
|
private |
Referenced by embvm::TimerManager< 0, std::mutex >::clearExpiredTimers().
◆ scheduled_q_lock_
|
private |
Referenced by embvm::TimerManager< 0, std::mutex >::addToScheduledQueue(), embvm::TimerManager< 0, std::mutex >::adjustScheduledTimerCount(), embvm::TimerManager< 0, std::mutex >::cancel(), embvm::TimerManager< 0, std::mutex >::clearExpiredTimers(), embvm::TimerManager< 0, std::mutex >::lockAndPopScheduledQueueFront(), embvm::TimerManager< 0, std::mutex >::sortScheduledQueue(), embvm::TimerManager< 0, std::mutex >::startNextTimer(), embvm::TimerManager< 0, std::mutex >::stopRunningTimer(), and embvm::TimerManager< 0, std::mutex >::~TimerManager().
◆ scheduled_queue_
|
private |
Referenced by embvm::TimerManager< 0, std::mutex >::addToScheduledQueue(), embvm::TimerManager< 0, std::mutex >::adjustScheduledTimerCount(), embvm::TimerManager< 0, std::mutex >::cancel(), embvm::TimerManager< 0, std::mutex >::clearExpiredTimers(), embvm::TimerManager< 0, std::mutex >::popScheduledQueueFront(), embvm::TimerManager< 0, std::mutex >::sortScheduledQueue(), and embvm::TimerManager< 0, std::mutex >::startNextTimer().
◆ timer_hw_
|
private |
Referenced by embvm::TimerManager< 0, std::mutex >::startNextTimer(), embvm::TimerManager< 0, std::mutex >::stopRunningTimer(), embvm::TimerManager< 0, std::mutex >::TimerInterruptHandler(), embvm::TimerManager< 0, std::mutex >::TimerManager(), and embvm::TimerManager< 0, std::mutex >::~TimerManager().
◆ timer_list_
|
private |
◆ timer_list_lock_
|
private |
◆ embvm::VirtualHwPlatformBase
| class embvm::VirtualHwPlatformBase |
template<typename THWPlatform>
class embvm::VirtualHwPlatformBase< THWPlatform >
Virtual Hardware Platform Base.
This class provides the common interfaces and behaviors that virtual hardware platforms must implement. Some functionality is common to all platforms (name functions).
Functions whose names are appended with _ are meant to be supplied by the derived hardware platform:
- earlyInitHook_()
- init_()
- initProcessor_()
- soft_reset_()
- hard_reset_()
- shutdown_()
Derived classes may supply additional functions as required. The functions above are the common required functions that all hardware platforms must supply.
This class uses the docs/development/patterns/crtp.md ["CRTP pattern"] rather than virtual inheritance. To derive from this class, do the following:
- Template Parameters
-
THWPlatform the derived HW platform implementation (CRTP pattern)
Public Member Functions | |
| VirtualHwPlatformBase (const char *name) noexcept | |
| Create a named virtual hardware platform. More... | |
| VirtualHwPlatformBase (const std::string &name) noexcept | |
| Create a named virtual hardware platform. More... | |
| VirtualHwPlatformBase (const std::string_view &name) noexcept | |
| Create a named virtual hardware platform. More... | |
| ~VirtualHwPlatformBase ()=default | |
| Default destructor. More... | |
| VirtualHwPlatformBase (const VirtualHwPlatformBase &)=delete | |
| Deleted copy constructor. More... | |
| const VirtualHwPlatformBase & | operator= (const VirtualHwPlatformBase &)=delete |
| Deleted copy assignment operator. More... | |
| VirtualHwPlatformBase (VirtualHwPlatformBase &&)=delete | |
| Deleted move constructor. More... | |
| VirtualHwPlatformBase & | operator= (VirtualHwPlatformBase &&)=delete |
| Deleted move assignment operator. More... | |
| constexpr const std::string_view & | name () const noexcept |
| Returns the Virtual HW Platform's name. More... | |
| constexpr const char * | name_cstr () const noexcept |
| Returns the platform name as a cstring for C API compatibility. More... | |
| void | initProcessor () noexcept |
| Initialize the processor. More... | |
| void | init () noexcept |
| Initialize the hardware platform. More... | |
| void | soft_reset () noexcept |
| Perform a soft reset of the system (chip reset) More... | |
| void | hard_reset () noexcept |
| Perform a hard reset of the system (power cycle) More... | |
| void | shutdown () noexcept |
| Shutdown the system. More... | |
Static Public Member Functions | |
| static void | earlyInitHook () noexcept |
| Perform any special initialization steps. More... | |
Private Attributes | |
| const std::string_view | name_ |
Constructor & Destructor Documentation
◆ VirtualHwPlatformBase() [1/5]
|
inlineexplicitnoexcept |
Create a named virtual hardware platform.
- Parameters
-
name C-string containing the hardware platform name
◆ VirtualHwPlatformBase() [2/5]
|
inlineexplicitnoexcept |
Create a named virtual hardware platform.
- Parameters
-
name std::string containing the hardware platform name Note: VirtualHwPlatformBase uses a std::string_view, so the std::string must remain valid throughout the lifetime of VirtualHwPlatformBase.
◆ VirtualHwPlatformBase() [3/5]
|
inlineexplicitnoexcept |
Create a named virtual hardware platform.
- Parameters
-
name std::string_view containing the hardware platform name Note: VirtualHwPlatformBase uses a std::string_view, so the std::string_view must remain valid throughout the lifetime of VirtualHwPlatformBase.
◆ ~VirtualHwPlatformBase()
|
default |
Default destructor.
◆ VirtualHwPlatformBase() [4/5]
|
delete |
Deleted copy constructor.
◆ VirtualHwPlatformBase() [5/5]
|
delete |
Deleted move constructor.
Member Function Documentation
◆ earlyInitHook()
|
inlinestaticnoexcept |
Perform any special initialization steps.
The earlyInitHook_() function must be implemented by the derived class as a static function.
These functions run before the C Run-time setup functions are called, and normal functionality (e.g. OS concepts) are not available.
Early initialization steps represent any super early code that needs to execute. For example, DRAM might need to be initialized before the boot process can relocate memory to its proper location in memory.
These functions are declared static to prevent you from easily using drivers within their confines
◆ hard_reset()
|
inlinenoexcept |
Perform a hard reset of the system (power cycle)
The hard_reset_() function must be implemented by the derived class.
A hard reset is intended to perform a full power cycle of the system.
Platforms which do not support a hard reset should default to calling soft_reset().
◆ init()
|
inlinenoexcept |
Initialize the hardware platform.
The init_() function must be implemented by the derived class.
Perform any hardware platform initialization steps, such as preparing peripherals for use, setting up callbacks, etc.
Referenced by nRF52DK_FrameworkDemoPlatform::initHWPlatform_(), FrameworkDemoSimPlatform::initHWPlatform_(), and UnitTestPlatform::initHWPlatform_().
◆ initProcessor()
|
inlinenoexcept |
Initialize the processor.
The initProcessor_() function must be implemented by the derived class.
Perform any steps necessary for initializing the processor & processor peripheral devices for use.
Note that this is only intended to be processor initialization. Platform initialization nis handled by the init() function.
This function will likely invoke the VirtualProcessor::init() function, but the order and actual initialization process is left to the derived class.
Referenced by nRF52DK_FrameworkDemoPlatform::initProcessor_(), FrameworkDemoSimPlatform::initProcessor_(), and UnitTestPlatform::initProcessor_().
◆ name()
|
inlinenoexcept |
Returns the Virtual HW Platform's name.
Referenced by UnitTestPlatform::hwPlatformName().
◆ name_cstr()
|
inlinenoexcept |
Returns the platform name as a cstring for C API compatibility.
Referenced by UnitTestPlatform::hwPlatformName_cstr().
◆ operator=() [1/2]
|
delete |
Deleted copy assignment operator.
◆ operator=() [2/2]
|
delete |
Deleted move assignment operator.
◆ shutdown()
|
inlinenoexcept |
Shutdown the system.
The shutdown_() function must be implemented by the derived class.
If your platform supports shutdown capability, take the proper steps to initiate a shutdown.
If the platform does not support shutdown capability, implement your shutdown_() function as an assert to notify users trying to call this API. You could also leave the shutdown_() function undefined. Anyone who calls the shutdown() function on a platform with an undefined shutdown_() function will encounter a compiler error.
The shutdown function is not expected to return.
◆ soft_reset()
|
inlinenoexcept |
Perform a soft reset of the system (chip reset)
The soft_reset_() function must be implemnted by the derived class.
A soft reset is intended to reset the program to the beginning without performing a full power cycle.
A good strategy is to just call virtual processor's reset() function, if one is provided.
Member Data Documentation
◆ name_
|
private |
 1.8.15
1.8.15